Exploring the Linux Filesystem
wubie@D-T430:~$ [On the bash prompt the tilde character represent the home directory]
- The pwd command for printing the working directory
Print the current working directory: with pwd command
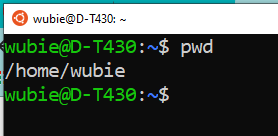
/home/wubie [ / is the root, i.e the beginning of the hard drive; home is a directory or folder under root (/); then wubie is a directory under home folder]
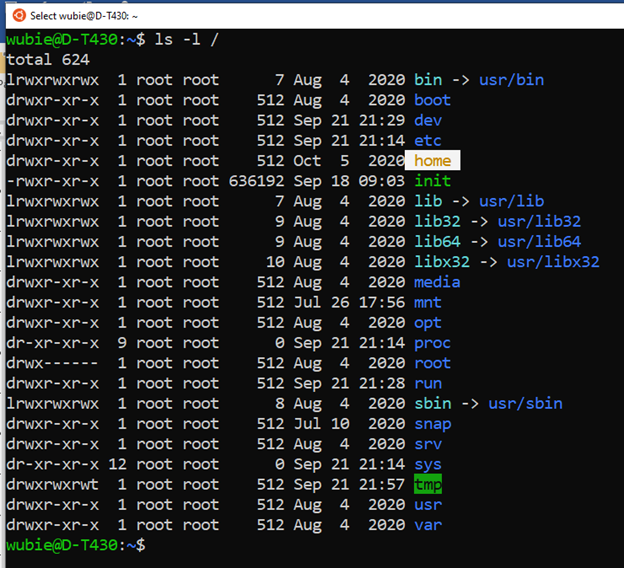
- The ls –l command for long listing
Long listing the files in the root can give you what is inside in the root: wubie@D-T430:~$ ls -l /
- The cd command to change directory:
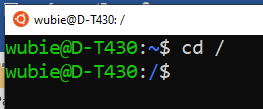
Use the cd command to change in to a different directory:
wubie@D-T430:~$ cd / [here we change from the home directory (~) to root directory [/]]
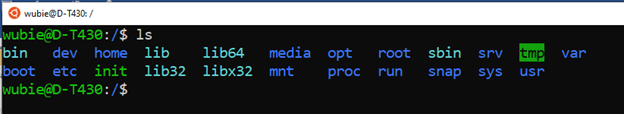
- The ls command for list storage
Listing what is inside the root directory use the command ls (list storage):
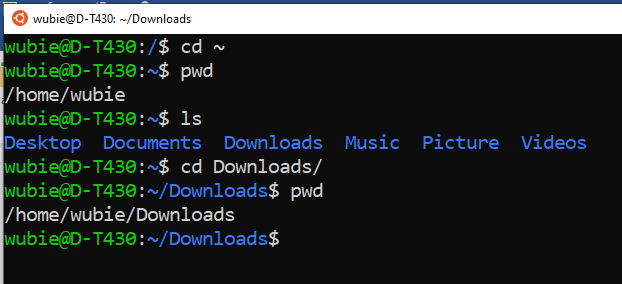
- Let us change directory from root to home;
- Then print the working directory;
- Then list what is inside the home directory;
- Then change directory to Downloads folder and
- Print the working directory:
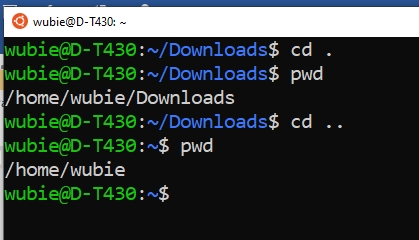
- The cd .. and cd . commands:
The cd .. command changes our directory one step backwards. The cd . command changes a directory to itself.
- The clear (Ctrl + l) command to clear the screen:
By doing a long listing of the root root of the file system:
The boot directory has important files that are used to boot up your machine.
wubie@D-T430:/$ ls /boot to see the files inside the boot directory that are useful to boot up the server or workstation.
Get back to my home directory:
wubie@D-T430:/$ cd home/wubie/ and wubie@D-T430:/$ cd ~ are the same.
cd ~ wherever you are you can go back to your home directory using the cd tilde command.
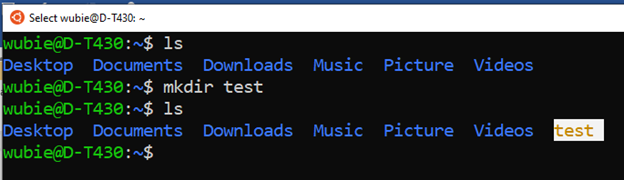
- The mkdir command to create a directory:
Creating a folder cold test:
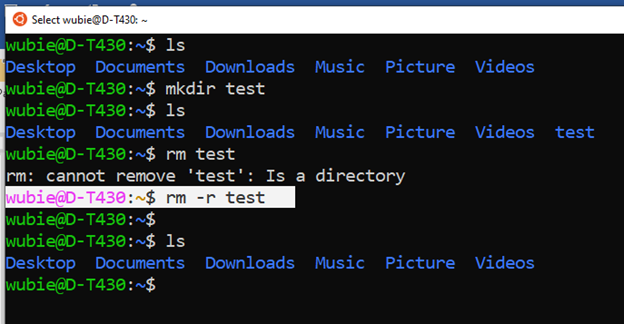
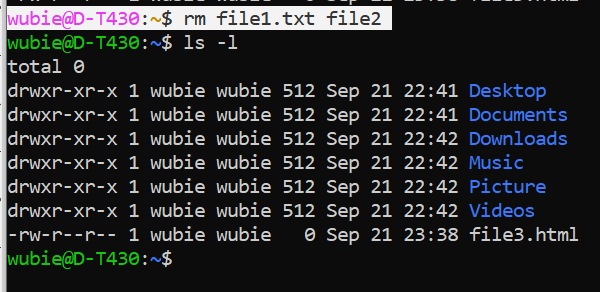
- The rm –r command to remove the directory ( -r is recursive):
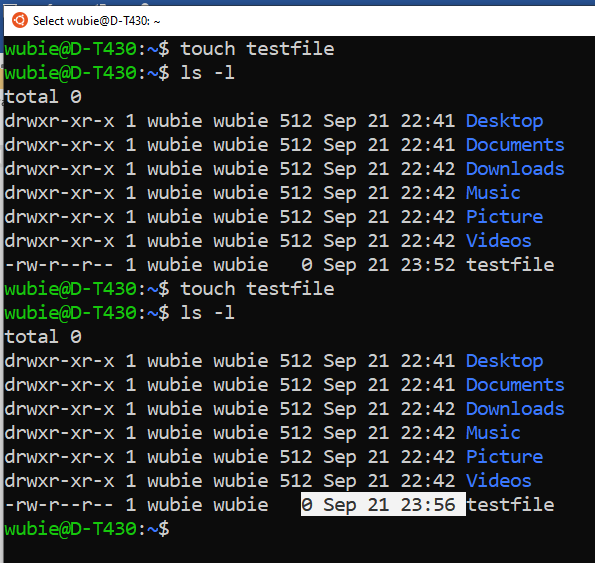
- The touch command to create files if it does not exist: If it already exists, it will update only the modification time.
- The directories start with a d character and the files start with a hyphen (-)
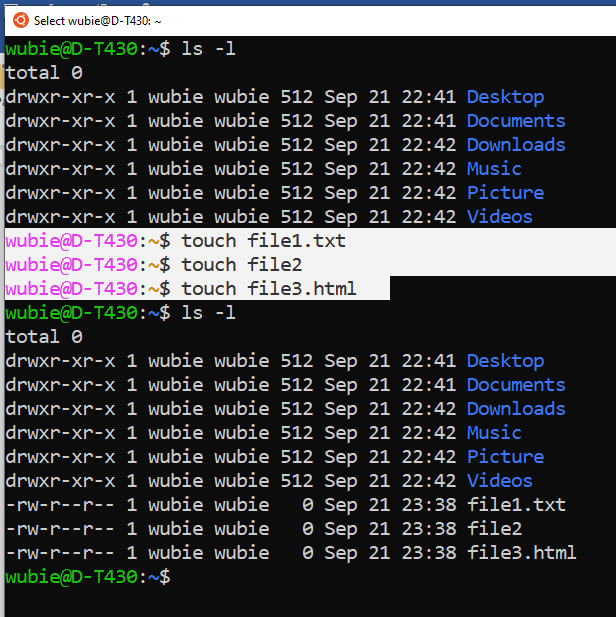
- The rm command to remove a file:
wubie@D-T430:~$ rm file1.txt file2 this will remove the two files at onece.
- Running the touch command creates the file if it does not exist.
- If we run a touch command against a file that already exist, will update the modification time.
Note: When using commands use the Tab Key to Autocomplete file and directory names.